I spent the five happiest years of my life in a morgue. As a forensic scientist in the Cleveland coroner’s office I analyzed gunshot residue on hands and clothing, hairs, fibers, paint, glass, DNA, blood and many other forms of trace evidence, as well as crime scenes. Now I'm a certified latent print examiner and CSI for a police department in Florida. I also write a series of forensic suspense novels, turning the day job into fiction. My books have been translated into six languages.
Sure, no problem. Please email me at lisa-black@live.com.
We’ll hold the scene as long as we need to get everything done, and that could be a day or two or three, but for a kidnapping it probably wouldn’t be more than a day, just enough to collect all the victim’s stuff, and collect fingerprints, hairs, fibers, anything that might belong to the kidnapper. We eventually get tired and want to go home (though we can go and come back, so long as it hasn’t been ‘released’) and the police department don’t really want to hold it longer then absolutely necessary, because they have a cop or two sitting there doing nothing but guarding the scene, and it takes them off the road. Hope that helps!
At my agency the chaplains are all civilians from local denominations.
Almost certainly, no. Unlike television, real forensic equipment is designed to test for certain things. For example the mass spectrometer in the toxicology department is set to test for illegal narcotics and not heavy metals such as arsenic. If arsenic is suspected, it could be detected with a different instrument or different parameters programmed into the same instrument. So I doubt there is any equipment that could be set up to detect microscopic amounts of photographic chemicals, if a photo would even shed any.
Antiques Dealer
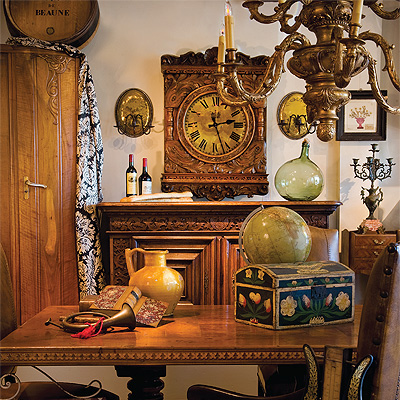 Does a piece's value increase significantly if it has a cool "back-story" to go along with it?
Does a piece's value increase significantly if it has a cool "back-story" to go along with it?
Las Vegas Cab Driver
 Do people ever ask you to keep your meter off in exchange for a cheaper fare?
Do people ever ask you to keep your meter off in exchange for a cheaper fare?
Cruise Ship Officer
 Is the "women and children first" rule still in effect?
Is the "women and children first" rule still in effect?
That’s a very broad question. What specifically do you need to know?
Wow, sorry, I have no idea where the subclavian vein even is. I’m afraid you need a pathologist.
Sorry I couldn’t be more help!
-OR-
 Login with Facebook
Login with Facebook (max 20 characters - letters, numbers, and underscores only. Note that your username is private, and you have the option to choose an alias when asking questions or hosting a Q&A.)
(A valid e-mail address is required. Your e-mail will not be shared with anyone.)
(min 5 characters)
By checking this box, you acknowledge that you have read and agree to Jobstr.com’s Terms and Privacy Policy.
-OR-
 Register with Facebook
Register with Facebook(Don't worry: you'll be able to choose an alias when asking questions or hosting a Q&A.)